Difference between revisions of "Habitat Systems"
Cslatlantis (Talk | contribs) m (→Other Engineering Systems: AYSE Docking Mechanism.. What was "Docking"?) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{NotCanon}} | + | {{Systems}}{{NotCanon}} |
<br> | <br> | ||
'''Habitat Systems''' refers to all of the components of the Habitat which are critical to its functioning including the Habitat itself. The development of high-quality systems is one of the [[OCESS]]'s main objectives, and their maintenance is critical to the well-being of the [[astronauts]] during the [[mission]]. | '''Habitat Systems''' refers to all of the components of the Habitat which are critical to its functioning including the Habitat itself. The development of high-quality systems is one of the [[OCESS]]'s main objectives, and their maintenance is critical to the well-being of the [[astronauts]] during the [[mission]]. | ||
Revision as of 15:02, 19 April 2010
| HS |
Habitat Systems refers to all of the components of the Habitat which are critical to its functioning including the Habitat itself. The development of high-quality systems is one of the OCESS's main objectives, and their maintenance is critical to the well-being of the astronauts during the mission.
The current Habitat configuration is the Hawking III.
Habitat Systems as described here and in all associated articles are considered to be in the Beta reality. Thus, while an article may describe the fusion reactors employed in the AYSE drive, it is understood that Spacesim does not actually possess this technology, and that these are merely simulated for the purposes of the mission.
Contents
Communication Systems
- Main article: Communications Systems
The Habitat uses both radio, laser, and IEST communications systems in order to maintain contact with Mission Control and transmit data back to Earth.
- Radio
- The radio system uses amplitude modulation, and is the primary method of voice communication.
- Laser
- The laser system is used to transmit text-based data and computer files to the SIMSAT communications satellite in Earth orbit.
- IEST
- The IEST is an experimental device based on the spin dynamics of electrons that is being developed to replace the Laser system.
Engineering Systems
- Main article: Engineering Systems
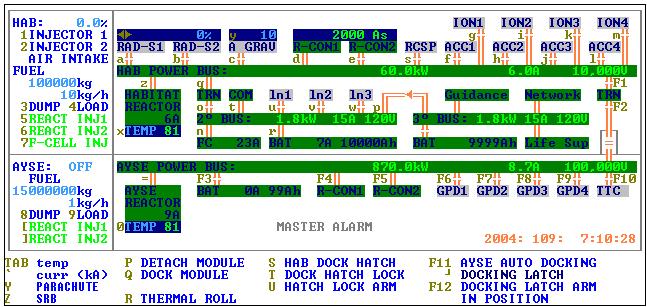
Power
- Habitat Reactor
- A pair of deuterium-tritium Tokamak Fusion reactors.
- Reactor Containment (R-CON1,2)
- AYSE Reactor
- Fuel Cell (FC)
- A hydrogen fuel cell.
- Batteries (BAT)
- Fuel
- Liquid Hydrogen.
Propulsion Systems
- Reaction Control Thrusters (RCSP)
- Vernier CO2 thruster system for attitude control
- Ionizers (ION1-4)
- Ionizes fuel to prepare it for the Accelerators
- Accelerators (ACC1-4)
- Accelerates ions created in the ionizers to produce thrust
- Graviton Projection Device (GPD1-4)
- Engine which generates quickly evaporating micro-singularities in front of the AYSE Drive
Other Engineering Systems
- Radiation Shields (RAD-S1, S2)
- System generates an electromagnetic field around the Habitat to divert oncoming radiation
- Artificial Gravity (A GRAV)
- Inertial dampening system to reduce acceleration strain on Habitat occupants and equipment
- Communications (COM)
- Power to the radio component of the Communications Systems
- Lights(ln1-3)
- Master switch for the lights in the 1) C&C, 2) Interlock and Hotlab, 3)Longhouse, Bathroom, and Airlock
- Transformers (TRN)
- Tranform voltages between power buses.
- Tachyon-Tardyon Collider TTC
- An archaic and now backup power generation system
- Solid Rocket Booster (SRB)
- Solid chemical propellant based booster for liftoff from Earth
- Parachutes
- AYSE Docking Mechanism
- Allows the Hab to power itself off of AYSE and to control the interplanetary drive.
- Life Support (Life Sup)
- Without power to Life Support, the Vents and Water Recycler will not operate.
Environmental Systems
- Main article: Environmental Systems
The Environmental Systems provide or control atmospheric pressure, fire detection and suppression, oxygen levels, waste management, and water supply. The Habitat is not an environmentally closed system.
- Vents
- High-powered fans move gasses in and out of modules
- Atmospheric Filters
- Various filters to scrub Dust, C02, and Humidity
- Water Recycler
- Low-efficiency water reclamation unit
- Fire Suppression
- Smoke Detectors and Extinguishers
- Waste Management
- Chemical Toilets (no water is reclaimed)
Hull & Superstructure
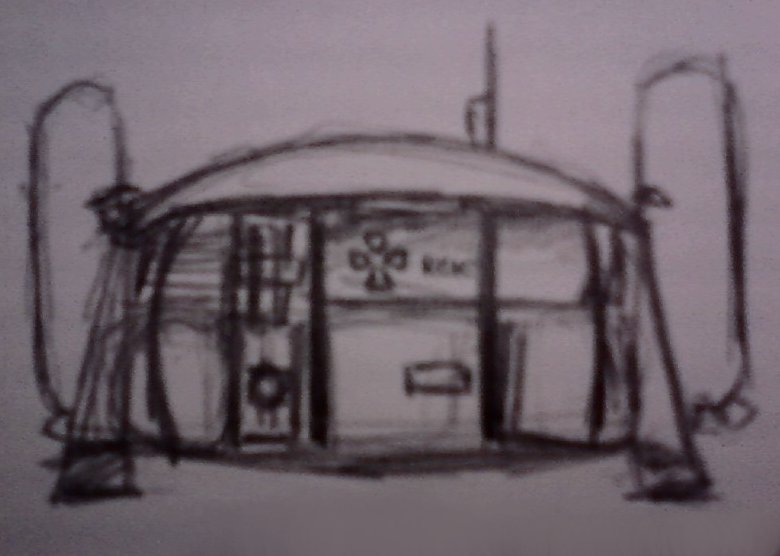
- Main article: Category:Hull & Superstructure
Hull and Superstructure refers to the overall physical design of the Habitat: its shape, subdivisions, and composition.
Shape
In outer shape, the Hawking III can be described as a rectangular prism of various modules tied together by a binding structure. A hemispherical dome is on the top and a metal strut sticks out near its center. A somewhat hemispherical heat-shield dome for re-entry is on the bottom. To each corner of the prism are protruding triangular shapes, pointing downwards, hosting the set of four positive-thrust ion engines and the landing gear. This configuration of the Habitat is depicted in the works of Spacesim artist Chen-tao LaRochelle.
Subdivisions
The interior of the Habitat is divided into three sections and two decks. The Pressurized Deck hosts the Hab Section and is where the astronauts live during the mission. The Unpressurized Deck contains the Engineering Section and the Storage Section, both inaccessible by the astronauts during the mission.
Pressurized Deck
- Main article: Pressurized Deck
The Pressurized deck is the Hab itself (Hab Section for organizational purposes) and it is located at the bottom of the superstructure. It is divided into seven modules, each with its own bulkhead and environmental controls. These modules are the Airlock, the Bathroom, Command and Control, the Engineering Closet, the Hotlab, the Interlock, and the Longhouse. Oxygen and Gravity are conveniently available in the Hab Section.
Unpressurized Deck
- Main article: Unpressurized Deck
The Unpressurized Deck of the Hawking III is located above the Hab and contains the Engineering Section and the Storage Section. The reactor, life support systems (Oxygen reserves, air scrubbers, etc..), AYSE docking, SRB clamps and EM-field generator form a quasi-deck in the Engineering Section. Just above are assembled the 4 water tanks and the ring of 10 compressed Hydrogen fuel tanks of the Storage Section, forming a rudimentary shield against certain radiations. It is inaccessible to the astronauts, but all controls are inside the Pressurized Deck, except for manual overrides.
Composition
- Main article: Hull Plating
The Habitat is protected by a series of ablative armour plates. These plates are laminated and spaced away from the Habitat, forming what is known as an "ablative spaced-laminate". It is a combination of several techniques used to protect tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles.
Wiki Project
- Main article: Category:Habitat Systems
Habitat Systems are the subject of a major wiki project, initiated by Alex Foo in 2006-07. The project seeks to define all of the systems used at Spacesim whereas the true definition of the technologies employed is often nebulous and fudged over with references to physics classes and science fiction. The project is ongoing as of April 2010.